Lean Principles with Technology in the Age of Digitization
- Jul 29, 2024
- 4 min read

Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, industries increasingly prioritise digitisation to remain competitive and efficient.
However, the true potential of digital transformation is unlocked when it is harmoniously integrated with lean principles.
Lean transformation focuses on minimising waste and maximising customer value, a philosophy that can be significantly amplified through the strategic use of technology.
This white paper explores how organisations can leverage lean principles in the digital age, uncovering distinctive yet impactful approaches that senior executives can implement to drive sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Key aspects of this article
The Intersection of Lean and Technology
Lean transformation and digital technology are not mutually exclusive; rather, they complement each other to create a robust framework for continuous improvement. By integrating technology with lean principles, organisations can enhance their ability to identify waste, streamline processes, and deliver superior value to customers.
Fundamental Lean Principles
Before delving into the integration of technology, it's essential to understand the fundamental lean principles that underpin successful transformations:
Value: Define value from the customer's perspective. Only activities that add value to the customer should be maintained.
Value Stream: Map all steps—value-adding and non-value-adding—needed to deliver the product or service to the customer and identify waste areas.
Flow: Ensure the value-creating steps flow smoothly without interruptions, delays, or bottlenecks.
Pull: Produce only what the customer needs when needed, reducing overproduction and inventory.
Perfection: Continuously improve processes to achieve perfection, aiming for zero waste and maximum efficiency.
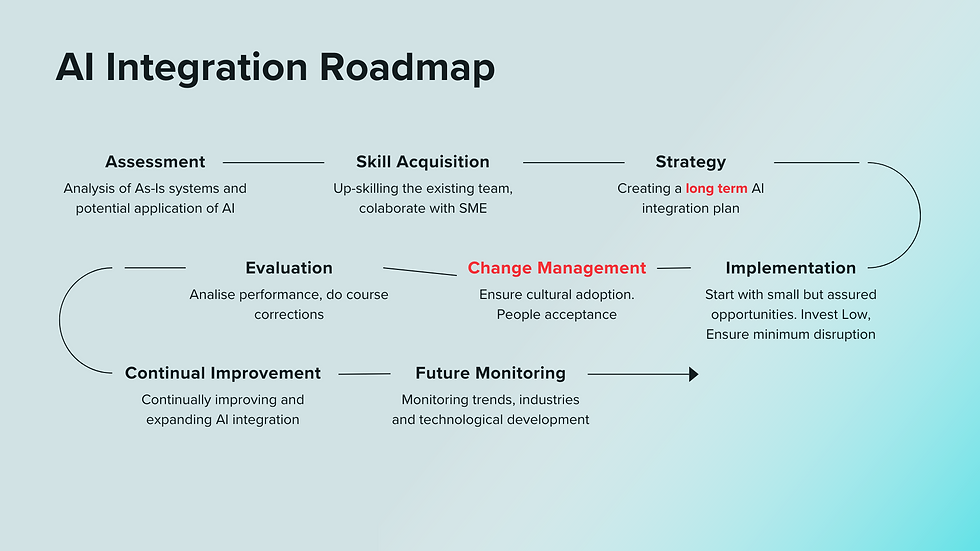
Integrating Lean Principles with Technology
Real-Time Data Analytics for Proactive Decision-Making
Traditional lean practices rely heavily on historical data and periodic reviews to identify inefficiencies. However, with advancements in real-time data analytics, organisations can now monitor processes continuously and make proactive decisions.
Real-time analytics tools can collect data from various sources, such as IoT devices and sensors, to provide instant insights into production line performance, equipment health, and supply chain dynamics.
Potential:
A manufacturing firm implemented real-time data analytics across its production lines. By continuously monitoring machine performance and production metrics, the firm could detect anomalies and potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach reduced downtime and increased overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Predictive Maintenance for Enhanced Equipment Reliability
Lean principles emphasise the importance of equipment reliability and minimising downtime. Predictive maintenance leverages machine learning algorithms to analyse data from equipment sensors and predict when maintenance is needed.
This approach prevents unexpected breakdowns and optimises maintenance schedules, ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
Potential:
An automotive manufacturer adopted predictive maintenance for its assembly lines. By analysing vibration, temperature, and other sensor data, the company could predict when critical components were likely to fail.
This strategy reduced unplanned maintenance and extended the lifespan of key machinery.
Digital Twin Technology for Process Optimization
Digital twin technology involves creating a virtual replica of physical assets, processes, or systems. This digital model allows organisations to simulate different scenarios, identify inefficiencies, and optimise processes without disrupting actual operations.
By integrating digital twins with lean principles, organisations can experiment with various lean strategies and identify the most effective ones before implementation.
Potential:
A chemical company used digital twin technology to model its entire production process. The company identified the most effective ways to reduce waste and improve throughput by simulating different lean initiatives.
Implementing these strategies in the physical plant increased production efficiency and waste reduction.
Augmented Reality (AR) for Workforce Training and Collaboration
Lean principles highlight the importance of a well-trained and engaged workforce. Augmented reality (AR) can revolutionise workforce training by providing immersive, hands-on experiences without the need for physical resources.
AR can also facilitate remote collaboration, allowing experts to guide on-site workers in real-time, reducing errors, and improving efficiency.
Potential:
An electronics manufacturer implemented AR-based training programs for its assembly line workers. The immersive training reduced onboarding time and decreased assembly errors.
Additionally, remote AR collaboration tools enabled experts to assist on-site workers, enhancing problem-solving and decision-making capabilities.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency and Efficiency
Lean supply chain management focuses on reducing waste and enhancing transparency. Blockchain technology provides an immutable ledger for tracking goods, ensuring traceability, and reducing fraud. By integrating blockchain with lean principles, organisations can achieve end-to-end visibility and streamline supply chain operations.
Potential:
A pharmaceutical company implemented blockchain technology to track its supply chain. This integration provided real-time visibility into the movement of raw materials and finished products, reducing lead times and improving overall supply chain transparency.
The company also enhanced its ability to respond to recalls and regulatory requirements, ensuring product safety and compliance.
Gamification for Continuous Improvement
Engaging employees in the lean transformation process is crucial for sustained success. Gamification involves applying game-design elements and principles in non-game contexts to motivate and increase participation. By gamifying lean initiatives, organisations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Potential:
A consumer goods company introduced a gamification platform where employees could earn points and rewards for submitting ideas, participating in lean workshops, and achieving improvement targets.
This initiative led to increased employee participation in lean activities and a significant boost in overall productivity.
AI-Driven Customer Feedback Analysis
Understanding customer value is at the heart of lean principles. AI-driven customer feedback analysis can sift through large volumes of customer feedback, reviews, and social media mentions to identify key insights and trends. This approach enables organisations to align their lean strategies with actual customer needs and preferences.
Potential:
A retail company used AI-driven analysis to monitor customer feedback across multiple channels. The insights revealed specific areas where customers were experiencing delays and dissatisfaction. The company improved customer satisfaction scores and increased repeat purchases by addressing these pain points through targeted lean initiatives.
Hyper-Automation for Streamlined Processes
Hyper-automation involves the use of advanced technologies like robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning, and artificial intelligence to automate complex business processes. When combined with lean principles, hyper-automation can significantly reduce manual intervention, eliminate errors, and enhance process efficiency.
Potential:
A financial services firm implemented hyper-automation to streamline its loan processing operations. By automating repetitive tasks and using AI to handle exceptions, the firm reduced processing times and increased accuracy, leading to a better customer experience and higher throughput.

Step-by-Step Sample Approach for Opportunity Identification, Solution Design, and Implementation in Lean Digital Transformation
Embarking on a lean digital transformation requires a structured approach to identify opportunities, design solutions, and implement changes effectively.
This involves not only technical and process changes but also managing the human aspects to ensure successful adoption and sustained improvements.
The following step-by-step guide provides a comprehensive framework for CXOs and senior executives to navigate this journey.
Opportunity Identification
Step 1: Conduct a Value Stream Mapping (VSM) Workshop
Objective: Identify all value-adding and non-value-adding activities within the process to uncover areas of waste.
Actions:
Assemble a cross-functional team.
Map the current state of the process from start to finish.
Identify value-adding steps, delays, bottlenecks, and sources of waste.
Outcome: A clear visualisation of the current state with highlighted areas for improvement.
Step 2: Analyse Data and Gather Insights
Objective: Use data-driven insights to pinpoint specific inefficiencies and performance gaps.
Actions:
Collect relevant data from existing systems (e.g., Log Book, Excel, ERP, MES).
Utilise real-time data analytics tools to gain deeper insights.
Conduct root cause analysis on identified issues.
Outcome: Data-backed identification of key opportunity areas for lean improvement.
Step 3: Benchmark Against Industry Best Practices
Objective: Understand how leading organisations in the industry address similar challenges.
Actions:
Research industry benchmarks and best practices.
Compare internal processes & systems with industry standards.
Identify gaps and potential areas for adopting best practices.
Outcome: A set of best practice benchmarks to guide the improvement journey.
Solution Design
Step 4: Define Lean Goals and Objectives
Objective: Establish clear and measurable goals for the lean transformation initiative.
Actions:
Align goals with the overall business strategy.
Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
Prioritise objectives based on impact and feasibility.
Outcome: Well-defined goals and objectives that provide direction and focus.
Step 5: Develop a Digital Transformation Roadmap
Objective: Create a comprehensive plan that integrates lean principles with digital technologies.
Actions:
Identify suitable digital technologies (e.g., IoT, AI, AR, blockchain) that align with lean goals.
Outline key milestones and phases of the transformation.
Define roles, responsibilities, and resource requirements.
Outcome: A detailed roadmap that outlines the path to lean digital transformation.
Step 6: Design Lean Solutions and Digital Integrations
Objective: Develop solutions that address identified opportunities using lean principles and digital technologies.
Actions:
Brainstorm and design lean solutions (e.g., process optimisation, waste elimination).
Integrate digital tools to enhance lean solutions (e.g., predictive maintenance, real-time analytics).
Validate solutions through simulations or pilot projects.
Outcome: A set of validated lean solutions integrated with digital technologies.
Implementation
Step 7: Prepare a Change Management Plan
Objective: Ensure the successful adoption of changes by addressing the human aspects.
Actions:
Conduct a stakeholder analysis to understand impacts and concerns.
Develop a communication plan to keep all stakeholders informed and engaged.
Create training programs to build necessary skills and knowledge.
Establish support mechanisms (e.g., change champions, help desks).
Outcome: A comprehensive change management plan that facilitates smooth implementation.
Step 8: Implement Lean Solutions and Digital Tools
Objective: Execute the designed solutions and integrate digital tools into the operations.
Actions:
Roll out solutions in a phased manner to manage risk and ensure control.
Monitor implementation progress and address any issues promptly.
Utilise digital tools to collect data and monitor performance in real-time.
Outcome: Successful deployment of lean solutions and digital tools, leading to initial improvements.
Step 9: Monitor and Sustain Improvements
Objective: Ensure that improvements are sustained and continuously enhanced.
Actions:
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
Implement regular review cycles to assess performance and identify further opportunities.
Encourage a culture of continuous improvement through ongoing training and engagement.
Outcome: Sustained improvements and a culture of continuous enhancement.
Change Management: A Critical Component
Effective change management is crucial to the success of any lean digital transformation. It ensures that the human aspect of change is addressed, promoting acceptance and minimising resistance.
Key Aspects of Change Management:
Leadership Engagement: Ensure leaders are visibly committed to the transformation and actively support the initiative.
Stakeholder Involvement: Engage stakeholders early and often, addressing their concerns and incorporating their feedback.
Communication: Maintain open and transparent communication throughout the process to build trust and keep everyone informed.
Training and Development: Provide comprehensive training to equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the new environment.
Support Systems: Establish support systems such as change champions, help desks, and feedback mechanisms to assist employees during the transition.
Conclusion
Fusing lean principles with advanced digital technologies offers a transformative approach to achieving operational excellence. By leveraging real-time data analytics, predictive maintenance, digital twin technology, augmented reality, blockchain, gamification, AI-driven customer feedback analysis, and hyper-automation, organisations can unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and customer value.
For CXOs, embracing this integrated approach is not just a strategic advantage but a necessity in the digital age. By staying ahead of the curve and continuously innovating, organisations can navigate the complexities of the modern business environment and achieve sustainable growth.
_edited_edited_edite.png)












Comments